Java Read Files From Beginning Again
File choosers provide a GUI for navigating the file system, and and so either choosing a file or directory from a list, or entering the proper noun of a file or directory. To display a file chooser, you lot normally use the JFileChooser API to show a modal dialog containing the file chooser. Another manner to present a file chooser is to add an instance of JFileChooser to a container.
Notation:
If you intend to distribute your programme every bit a sandbox Java Web Start awarding, and then instead of using the JFileChooser API you should utilise the file services provided by the JNLP API. These services — FileOpenService and FileSaveService — not just provide back up for choosing files in a restricted environs, but as well accept intendance of really opening and saving them. An example of using these services is in JWSFileChooserDemo. Documentation for using the JNLP API can be found in the Java Spider web Start lesson.
Click the Launch push button to run JWSFileChooserDemo using Coffee™ Web Start (download JDK 7 or after). Alternatively, to compile and run the example yourself, consult the instance index.
![]()
When working with the JWSFileChooserDemo instance, be careful not to lose files that you need. Whenever y'all click the save push and select an existing file, this demo brings up the File Exists dialog box with a request to replace the file. Accepting the request overwrites the file.
The rest of this section discusses how to use the JFileChooser API. A JFileChooser object merely presents the GUI for choosing files. Your program is responsible for doing something with the called file, such equally opening or saving it. Refer to Basic I/O for data on how to read and write files.
The JFileChooser API makes information technology easy to bring up open and salve dialogs. The blazon of await and feel determines what these standard dialogs expect like and how they differ. In the Coffee wait and feel, the save dialog looks the same as the open dialog, except for the title on the dialog's window and the text on the push button that approves the operation. Here is a picture of a standard open dialog in the Java expect and feel:

Here is a picture of an awarding called FileChooserDemo that brings up an open dialog and a relieve dialog.
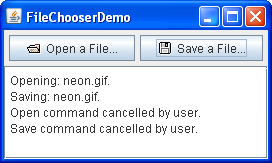
Try this:
- Compile and run the instance, consult the example index.
- Click the Open a File button. Navigate effectually the file chooser, choose a file, and click the dialog'due south Open button.
- Use the Save a File push button to bring up a relieve dialog. Try to use all of the controls on the file chooser.
- In the source file
FileChooserDemo.java, modify the file selection manner to directories-but manner. (Search forDIRECTORIES_ONLYand uncomment the line that contains it.) Then compile and run the example once more. You lot will only exist able to see and select directories, non ordinary files.
Bringing upwards a standard open dialog requires only 2 lines of code:
//Create a file chooser final JFileChooser fc = new JFileChooser(); ... //In response to a button click: int returnVal = fc.showOpenDialog(aComponent);
The statement to the showOpenDialog method specifies the parent component for the dialog. The parent component affects the position of the dialog and the frame that the dialog depends on. For example, the Java expect and experience places the dialog directly over the parent component. If the parent component is in a frame, and then the dialog is dependent on that frame. This dialog disappears when the frame is minimized and reappears when the frame is maximized.
Past default, a file chooser that has not been shown before displays all files in the user's home directory. You can specify the file chooser's initial directory by using one of JFileChooser's other constructors, or you can set up the directory with the setCurrentDirectory method.
The call to showOpenDialog appears in the actionPerformed method of the Open a File button's activity listener:
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { //Handle open up push action. if (e.getSource() == openButton) { int returnVal = fc.showOpenDialog(FileChooserDemo.this); if (returnVal == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION) { File file = fc.getSelectedFile(); //This is where a real application would open up the file. log.append("Opening: " + file.getName() + "." + newline); } else { log.append("Open control cancelled by user." + newline); } } ... } The proveXxxDialog methods return an integer that indicates whether the user selected a file. Depending on how yous use a file chooser, it is oftentimes sufficient to cheque whether the return value is APPROVE_OPTION and and then not to change any other value. To become the called file (or directory, if you ready the file chooser to allow directory selections), call the getSelectedFile method on the file chooser. This method returns an case of File.
The example obtains the proper noun of the file and uses information technology in the log message. You can call other methods on the File object, such equally getPath, isDirectory, or exists to obtain information most the file. You can likewise call other methods such as delete and rename to change the file in some mode. Of course, you might besides want to open or save the file by using ane of the reader or writer classes provided past the Java platform. See Basic I/O for data nigh using readers and writers to read and write data to the file system.
The example program uses the same instance of the JFileChooser grade to display a standard salve dialog. This time the program calls showSaveDialog:
int returnVal = fc.showSaveDialog(FileChooserDemo.this);
By using the aforementioned file chooser instance to brandish its open up and save dialogs, the programme reaps the following benefits:
- The chooser remembers the current directory betwixt uses, so the open up and salve versions automatically share the same current directory.
- You accept to customize only one file chooser, and the customizations apply to both the open and save versions.
Finally, the example program has commented-out lines of code that let you change the file selection mode. For example, the following line of code makes the file chooser able to select only directories, and not files:
fc.setFileSelectionMode(JFileChooser.DIRECTORIES_ONLY);
Another possible option style is FILES_AND_DIRECTORIES. The default is FILES_ONLY. The following film shows an open dialog with the file selection mode fix to DIRECTORIES_ONLY. Notation that, in the Coffee expect and feel at least, only directories are visible — not files.
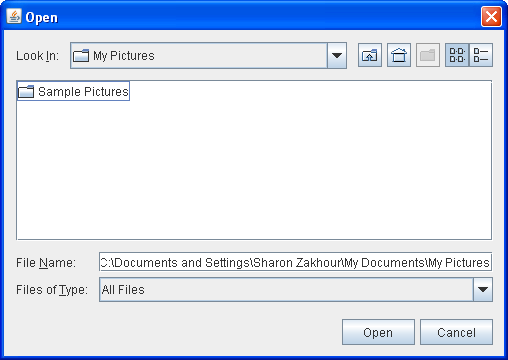
If you lot want to create a file chooser for a task other than opening or saving, or if you want to customize the file chooser, proceed reading. We volition hash out the following topics:
- Some other Example: FileChooserDemo2
- Using a File Chooser for a Custom Task
- Filtering the List of Files
- Customizing the File View
- Providing an Accessory Component
- The File Chooser API
- Examples that Employ File Choosers
Another Case: FileChooserDemo2
Allow usa wait at FileChooserDemo2 example, a modified version of the previous demo program that uses more than of the JFileChooser API. This example uses a file chooser that has been customized in several means. Like the original case, the user invokes a file chooser with the push of a button. Here is a picture of the file chooser:
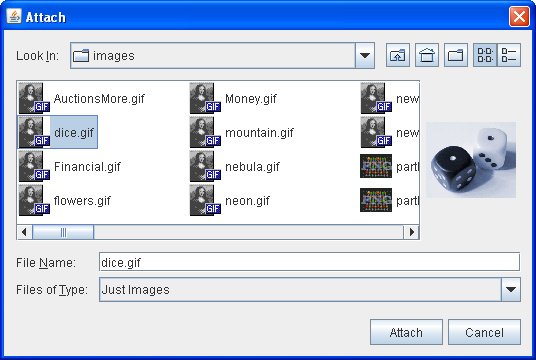
Every bit the figure shows, this file chooser has been customized for a special task (Attach), provides a user-choosable file filter (Just Images), uses a special file view for prototype files, and has an accessory component that displays a thumbnail sketch of the currently selected image file.
The residual of this section shows you the code that creates and customizes this file chooser. See the example index for links to all the files required past this example.
Using a File Chooser for a Custom Task
As you have seen, the JFileChooser course provides the showOpenDialog method for displaying an open dialog and the showSaveDialog method for displaying a save dialog.
The class has another method, showDialog, for displaying a file chooser for a custom task in a dialog. In the Coffee look and feel, the simply difference betwixt this dialog and the other file chooser dialogs is the title on the dialog window and the characterization on the approve push. Hither is the code from FileChooserDemo2 that brings upward the file chooser dialog for the Attach task:
JFileChooser fc = new JFileChooser(); int returnVal = fc.showDialog(FileChooserDemo2.this, "Attach");
The beginning statement to the showDialog method is the parent component for the dialog. The second argument is a String object that provides both the championship for the dialog window and the label for the approve button.
In one case once again, the file chooser doesn't do anything with the selected file. The program is responsible for implementing the custom job for which the file chooser was created.
Filtering the List of Files
Past default, a file chooser displays all of the files and directories that it detects, except for hidden files. A program tin utilise one or more file filters to a file chooser so that the chooser shows just some files. The file chooser calls the filter's accept method for each file to determine whether information technology should be displayed. A file filter accepts or rejects a file based on criteria such as file type, size, ownership, so on. Filters bear on the list of files displayed past the file chooser. The user can enter the name of whatsoever file even if it is not displayed.
JFileChooser supports iii different kinds of filtering. The filters are checked in the order listed hither. For example, an application-controlled filter sees only those files accepted by the born filtering.
- Congenital-in filtering
- Filtering is gear up upwards through specific method calls on a file chooser. Currently the just congenital-in filter bachelor is for subconscious files, such equally those whose names begin with period (.) on UNIX systems. By default, subconscious files are non shown. Telephone call
setFileHidingEnabled(false)to bear witness hidden files. - Awarding-controlled filtering
- The awarding determines which files are shown. Create a custom subclass of
FileFilter, instantiate it, and use the example as an argument to thesetFileFiltermethod. The installed filter is displayed on the list of user-choosable filters. The file chooser shows merely those files that the filter accepts. - User-choosable filtering
- The file chooser GUI provides a list of filters that the user can choose from. When the user chooses a filter, the file chooser shows only those files accepted by that filter.
FileChooserDemo2adds a custom file filter to the list of user-choosable filters:Past default, the list of user-choosable filters includes the Accept All filter, which enables the user to run into all non-hidden files. This case uses the following code to disable the Have All filter:fc.addChoosableFileFilter(new ImageFilter());
Our custom file filter is implemented infc.setAcceptAllFileFilterUsed(simulated);
ImageFilter.javaand is a subclass ofFileFilter. TheImageFilterclass implements thegetDescriptionmethod to return "Simply Images" — a string to put in the list of user-choosable filters.ImageFilteralso implements thehavemethod so that information technology accepts all directories and whatsoever file that has a.png,.jpg,.jpeg,.gif,.tif, or.tifffilename extension.By accepting all directories, this filter allows the user to navigate effectually the file system. If the assuming lines were omitted from this method, the user would be express to the directory with which the chooser was initialized.public boolean take(File f) { if (f.isDirectory()) { return true; } String extension = Utils.getExtension(f); if (extension != nil) { if (extension.equals(Utils.tiff) || extension.equals(Utils.tif) || extension.equals(Utils.gif) || extension.equals(Utils.jpeg) || extension.equals(Utils.jpg) || extension.equals(Utils.png)) { return true; } else { return false; } } render false; }The preceding code sample uses the
getExtensionmethod and several string constants fromUtils.coffee, shown here:public form Utils { public final static String jpeg = "jpeg"; public final static Cord jpg = "jpg"; public final static String gif = "gif"; public final static String tiff = "tiff"; public final static String tif = "tif"; public final static String png = "png"; /* * Get the extension of a file. */ public static String getExtension(File f) { String ext = nada; Cord southward = f.getName(); int i = due south.lastIndexOf('.'); if (i > 0 && i < s.length() - 1) { ext = south.substring(i+1).toLowerCase(); } render ext; } }
Customizing the File View
In the Java await and experience, the chooser's listing shows each file's name and displays a small icon that represents whether the file is a true file or a directory. Y'all can customize this file view by creating a custom subclass of FileView and using an example of the course as an argument to the setFileView method. The example uses an instance of a custom grade, implemented in ImageFileView.coffee, every bit the file chooser's file view.
fc.setFileView(new ImageFileView());
The ImageFileView grade shows a unlike icon for each type of epitome accustomed by the image filter described previously.
The ImageFileView course overrides the 5 abstract methods defined in the FileView as follows.
-
String getTypeDescription(File f) - Returns a description of the file type. Hither is
ImageFileView's implementation of this method:public String getTypeDescription(File f) { String extension = Utils.getExtension(f); String type = null; if (extension != zip) { if (extension.equals(Utils.jpeg) || extension.equals(Utils.jpg)) { type = "JPEG Image"; } else if (extension.equals(Utils.gif)){ type = "GIF Epitome"; } else if (extension.equals(Utils.tiff) || extension.equals(Utils.tif)) { type = "TIFF Paradigm"; } else if (extension.equals(Utils.png)){ type = "PNG Image"; } } return type; } -
Icon getIcon(File f) - Returns an icon representing the file or its type. Here is
ImageFileView's implementation of this method:public Icon getIcon(File f) { String extension = Utils.getExtension(f); Icon icon = nada; if (extension != nada) { if (extension.equals(Utils.jpeg) || extension.equals(Utils.jpg)) { icon = jpgIcon; } else if (extension.equals(Utils.gif)) { icon = gifIcon; } else if (extension.equals(Utils.tiff) || extension.equals(Utils.tif)) { icon = tiffIcon; } else if (extension.equals(Utils.png)) { icon = pngIcon; } } return icon; } -
Cord getName(File f) - Returns the proper noun of the file. About implementations of this method should return
nadato indicate that the expect and feel should figure information technology out. Another common implementation returnsf.getName(). -
String getDescription(File f) - Returns a description of the file. The intent is to depict individual files more specifically. A common implementation of this method returns
nullto indicate that the expect and feel should figure it out. -
Boolean isTraversable(File f) - Returns whether a directory is traversable. Virtually implementations of this method should return
zipto betoken that the await and feel should figure it out. Some applications might want to prevent users from descending into a certain type of directory considering information technology represents a chemical compound certificate. TheisTraversablemethod should never returntruefor a non-directory.
Providing an Accessory Component
The customized file chooser in FileChooserDemo2 has an accessory component. If the currently selected particular is a PNG, JPEG, TIFF, or GIF image, the accessory component displays a thumbnail sketch of the image. Otherwise, the accessory component is empty. Aside from a previewer, probably the well-nigh common utilise for the accompaniment component is a console with more than controls on it such as check boxes that toggle betwixt features.
The example calls the setAccessory method to found an instance of the ImagePreview class, implemented in ImagePreview.java, as the chooser'due south accompaniment component:
fc.setAccessory(new ImagePreview(fc));
Any object that inherits from the JComponent class can be an accompaniment component. The component should have a preferred size that looks proficient in the file chooser.
The file chooser fires a property alter result when the user selects an detail in the list. A plan with an accessory component must register to receive these events to update the accompaniment component whenever the option changes. In the example, the ImagePreview object itself registers for these events. This keeps all the code related to the accessory component together in one course.
Hither is the case's implementation of the propertyChange method, which is the method chosen when a property modify event is fired:
//where fellow member variables are alleged File file = null; ... public void propertyChange(PropertyChangeEvent east) { boolean update = false; String prop = east.getPropertyName(); //If the directory changed, don't show an image. if (JFileChooser.DIRECTORY_CHANGED_PROPERTY.equals(prop)) { file = null; update = truthful; //If a file became selected, find out which i. } else if (JFileChooser.SELECTED_FILE_CHANGED_PROPERTY.equals(prop)) { file = (File) e.getNewValue(); update = true; } //Update the preview accordingly. if (update) { thumbnail = null; if (isShowing()) { loadImage(); repaint(); } } } If SELECTED_FILE_CHANGED_PROPERTY is the belongings that changed, this method obtains a File object from the file chooser. The loadImage and repaint methods utilise the File object to load the image and repaint the accessory component.
The File Chooser API
The API for using file choosers falls into these categories:
- Creating and Showing the File Chooser
- Selecting Files and Directories
- Navigating the File Chooser'southward List
- Customizing the File Chooser
| Method or Constructor | Purpose |
|---|---|
| JFileChooser() JFileChooser(File) JFileChooser(String) | Creates a file chooser case. The File and String arguments, when nowadays, provide the initial directory. |
| int showOpenDialog(Component) int showSaveDialog(Component) int showDialog(Component, String) | Shows a modal dialog containing the file chooser. These methods return APPROVE_OPTION if the user approved the operation and CANCEL_OPTION if the user cancelled it. Another possible return value is ERROR_OPTION, which ways an unanticipated mistake occurred. |
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| void setSelectedFile(File) File getSelectedFile() | Sets or obtains the currently selected file or (if directory selection has been enabled) directory. |
| void setSelectedFiles(File[]) File[] getSelectedFiles() | Sets or obtains the currently selected files if the file chooser is set to permit multiple pick. |
| void setFileSelectionMode(int) void getFileSelectionMode() boolean isDirectorySelectionEnabled() boolean isFileSelectionEnabled() | Sets or obtains the file choice mode. Acceptable values are FILES_ONLY (the default), DIRECTORIES_ONLY, and FILES_AND_DIRECTORIES.Interprets whether directories or files are selectable according to the current option manner. |
| void setMultiSelectionEnabled(boolean) boolean isMultiSelectionEnabled() | Sets or interprets whether multiple files tin can be selected at one time. Past default, a user tin can cull only one file. |
| void setAcceptAllFileFilterUsed(boolean) boolean isAcceptAllFileFilterUsed() | Sets or obtains whether the AcceptAll file filter is used as an allowable option in the choosable filter listing; the default value is truthful. |
| Dialog createDialog(Component) | Given a parent component, creates and returns a new dialog that contains this file chooser, is dependent on the parent's frame, and is centered over the parent. |
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| void ensureFileIsVisible(File) | Scrolls the file chooser'south listing such that the indicated file is visible. |
| void setCurrentDirectory(File) File getCurrentDirectory() | Sets or obtains the directory whose files are displayed in the file chooser's listing. |
| void changeToParentDirectory() | Changes the listing to display the current directory'southward parent. |
| void rescanCurrentDirectory() | Checks the file system and updates the chooser's listing. |
| void setDragEnabled(boolean) boolean getDragEnabled() | Sets or obtains the belongings that determines whether automatic elevate treatment is enabled. See Elevate and Drop and Data Transfer for more details. |
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| void setAccessory(javax.swing.JComponent) JComponent getAccessory() | Sets or obtains the file chooser'south accessory component. |
| void setFileFilter(FileFilter) FileFilter getFileFilter() | Sets or obtains the file chooser'southward primary file filter. |
| void setFileView(FileView) FileView getFileView() | Sets or obtains the chooser's file view. |
| FileFilter[] getChoosableFileFilters() void addChoosableFileFilter(FileFilter) boolean removeChoosableFileFilter(FileFilter) void resetChoosableFileFilters() FileFilter getAcceptAllFileFilter() | Sets, obtains, or modifies the list of user-choosable file filters. |
| void setFileHidingEnabled(boolean) boolean isFileHidingEnabled() | Sets or obtains whether hidden files are displayed. |
| void setControlButtonsAreShown(boolean) boolean getControlButtonsAreShown() | Sets or obtains the property that indicates whether the Approve and Cancel buttons are shown in the file chooser. This property is true by default. |
Examples That Use File Choosers
This table shows the examples that use file choosers and points to where those examples are described.
| Instance | Where Described | Notes |
|---|---|---|
FileChooserDemo | This section | Displays an open dialog and a salvage dialog. |
FileChooserDemo2 | This section | Uses a file chooser with custom filtering, a custom file view, and an accessory component. |
JWSFileChooserDemo | This department | Uses the JNLP API to open and save files. |
toliveranempon1992.blogspot.com
Source: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/uiswing/components/filechooser.html
0 Response to "Java Read Files From Beginning Again"
Post a Comment